Fuel injection system – check
Note: The following procedure is based on the assumption that the fuel pressure is adequate (Fuel pump/fuel pressure – check).
1. Inspect all electrical connectors that are related to the system. Check the ground wire connections on the intake manifold for tightness. Loose connectors and poor grounds can cause many problems that resemble more serious malfunctions.
2. Verify that the battery is fully charged, as the control unit and sensors depend on an accurate supply of voltage in order to properly meter the fuel.
3. Inspect the air filter element (see Tune-up and routine maintenance). A dirty or partially blocked filter will severely impede performance.
4. Check the related fuses. If a blown fuse is found, replace it and see if it blows again. If it does, search for a grounded wire in the harness.
5. Inspect the condition of all vacuum hoses connected to the intake manifold.
6. Remove the air intake duct and air resonator box and inspect the mouth of the throttle body for dirt, carbon or other residue build-up. If it’s dirty, clean with a shop towel and a solvent specifically made for throttle bodies.
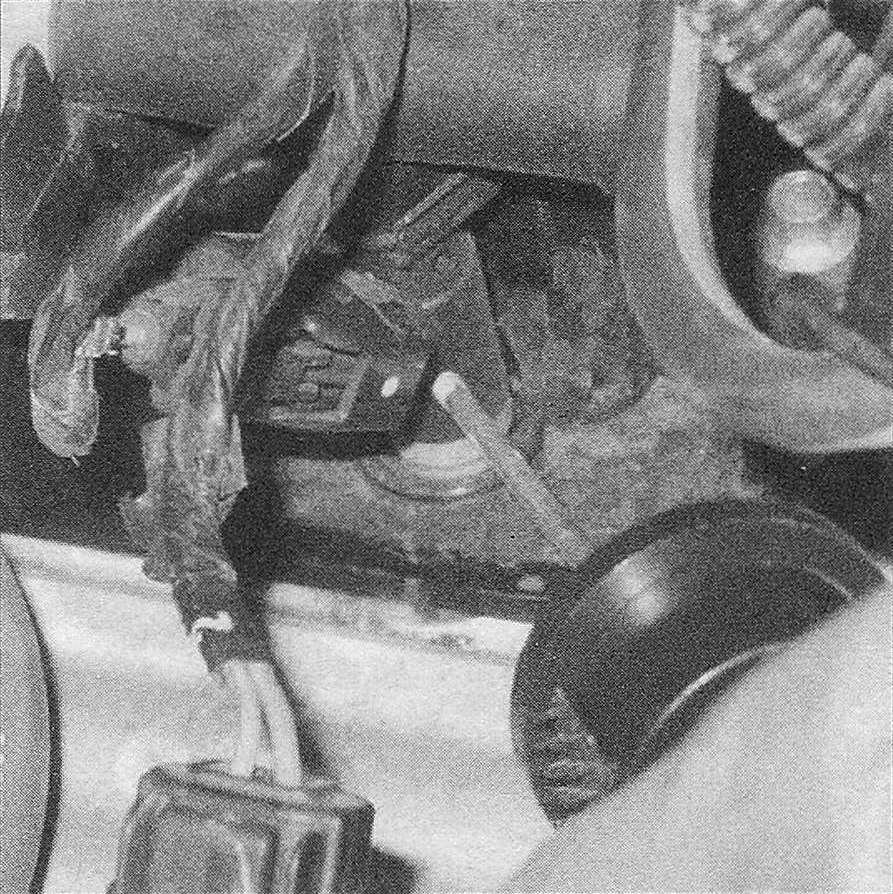
7. With the engine running, place an automotive stethoscope against each injector, one at a time, and listen for a clicking sound, indicating operation (see illustration). If you don’t have a stethoscope, place the tip of a screwdriver against the injector and listen through the handle.
10.7 Use a stethoscope to determine if the injectors are working properly – they should make a steady clicking sound that rises and falls with engine speed changes
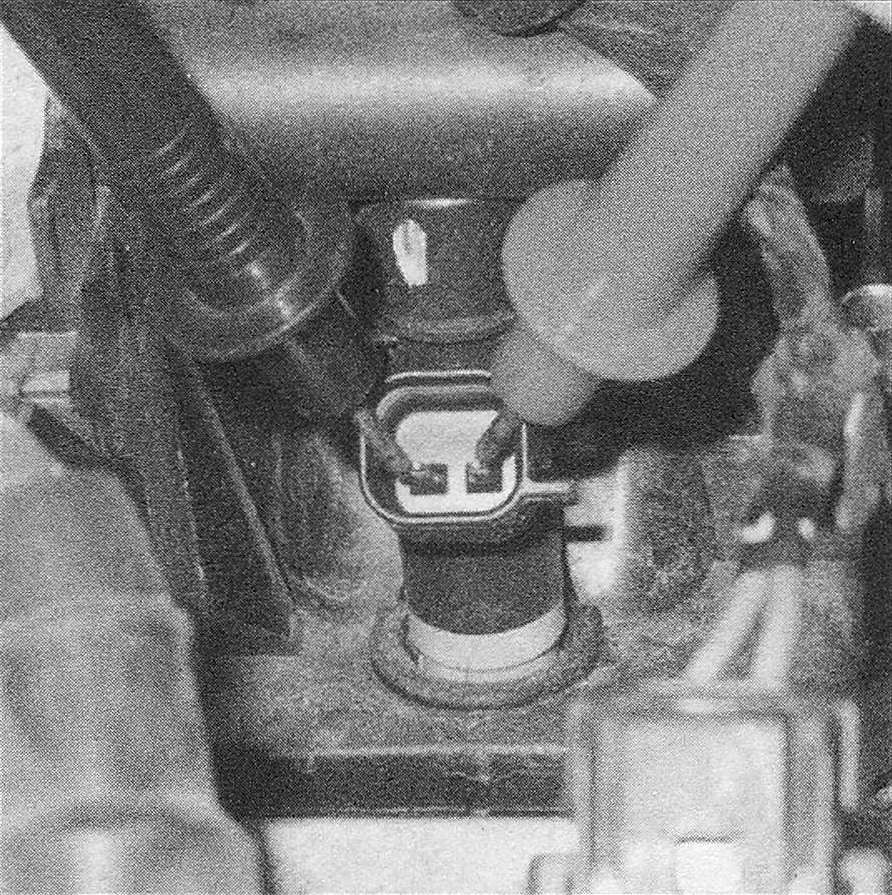
8. If an injector doesn’t make a clicking sound, disconnect the electrical connector and measure the resistance of the injector (see illustration). Compare the measurement with the resistance values of the other injectors. If it varies significantly from the others, it is probably defective. If the resistance is similar, the PCM or the injector wiring harness could be the cause of the injector not operating.
10.8 If you discover an injector that doesn’t appear to be operating, measure the resistance across the two terminals of the injector to see if the injector itself is defective
9. Any further testing of the fuel injection system should be performed at a dealer service department or other qualified repair shop.
10. For more information about the engine control system, refer to Chapter Emissions and engine control systems.